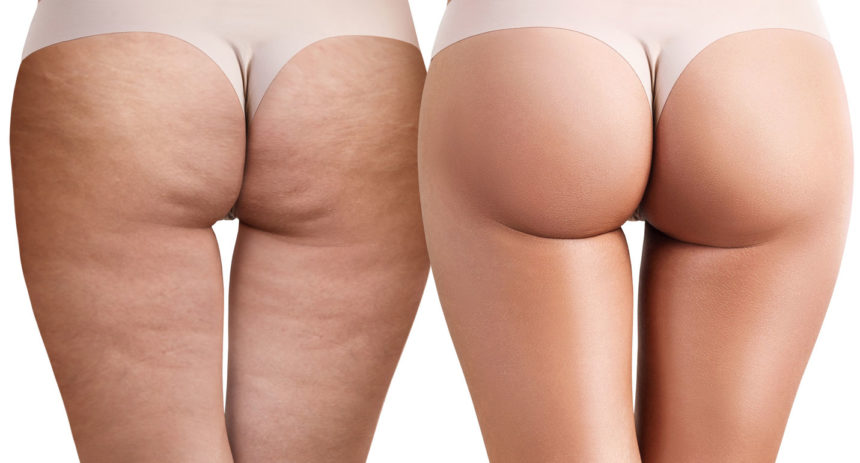
Cellulite is inflammatory degeneration of the subcutaneous adipose tissue with associated alteration of the structures of the supporting connective tissue, which gives the skin the unsightly orange-peel appearance.
Cellulite is caused by a complex series of factors that cause a venous and lymphatic stasis of the tissue. In particular, the arrangement that the cells take on has an impact, along with hormones and vascularisation, bad diet and a sedentary lifestyle.
So where do you start in combatting cellulite and how can you treat it? First of all, by preventing it and then by adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes:
- Food: eating vegetables and fruit, drinking plenty of water and keeping your weight under control without putting on or losing weight too quickly;
- Sport and physical exercise boost circulation and allow the oxygenation of tissues: sustained walking and exercises like step-ups, squats, lunges and those that allow aerobic movement of buttocks and thighs are highly recommended;
- You should not do extreme training as these involve the production of lactic acid which compromises the reactivation we are looking for;
- Do not wear very tight clothes which block the circulation and favour the stagnation of fluids;
- Use anatomical shoes to ensure correct posture and suitable arch support
- Cut out smoking and alcohol.
- Don’t stay in the same position for too long.
Various aesthetic medical treatments should be added to this, depending on the type of cellulite present. In fact, a distinction should be made between localised adiposity, i.e. when the adipose tissue increases in volume due to adipocyte hyperplasia, keeping the typical lumpiness and normal vascularisation and therefore easier to treat, and edematous fibrosclerotic panniculopathy which calls for complex procedures that help these elements disappear.
Mesotherapy
Techniques for fighting cellulite include mesotherapy, a technique that involves the injection of lipolytic or other substances with an emulsifying activity, as well as others that will stimulate the circulation and try to reduce stress and therefore cellulite. This method can cause several side effects including infections, rashes and blemishes or swelling on the surface of the skin.
Radiofrequency
Then there is radiofrequency which, by generating heat in the deep dermal layer, activates the production of new collagen fibres and visibly improves the quality of skin firmness. The treatments must be repeated over time, because the results are not permanent. The side effects are mild and range from redness to minor oedema.
Cryotherapy
We also offer cryotherapy which kills off the adipocytes through the application of a cold handpiece on the affected area. It also reduces inflammation and swelling while increasing blood flow to maintain thermal balance. This element is important for allowing disposal of the adipose matter that is broken down.
Medical cavitation
We can also consider cavitation, a treatment with a lipoclasic action that allows a reduction in the consistency of the fat and therefore progressive remodelling of the body shape. A solution is introduced into the panniculus adiposus and then, through the passage of ultrasound waves at a low frequency but high intensity, the macromolecules are charged with energy; these macromolecules burst, creating bubbles of vapour. The continuous formation and bursting of micro-bubbles function like shock waves, with energy that can alter the surrounding tissues. When it occurs near the adipocytes, this energy leads to the breakdown of the adipocyte walls, releasing the fatty acids. The disposal of the fragments produced is then carried out through physiological processes.
Electrolipolysis
Electrolipolysis is also effective against cellulite. Through an electric gradient applied through needles to the fluid that separates the adipocytes, it creates variations in internal ionic concentrations that help break these cells down, disposal of the excess fluids and with them also the by-products of the breakdown of fat.
Carboxytherapy
Carboxytherapy is another method through which carbon dioxide is administered subcutaneously and stimulates the regeneration of vessels that ensures a draining effect, thus decreasing swelling and hollows of the skin and oxygenates the tissues, restoring elasticity to the skin.
Liposuction
The fat deposits of cellulite can also be treated with the surgical techniques of liposuction, which is the removal of part of the subcutaneous adipose tissue through a suction cannula. Technology today allows us to obtain greater results; technological solutions combined with ultrasound or laser make it easier to dissolve the fat.
The latest innovation is laser lysis, through which a very thin sterile cannula is inserted directly into the fat; the optical fibre laser is passed through the cannula and, under its beam, the adipocytes are destroyed. At the same time, it closes the vessels, avoiding blood loss and stimulates the production of collagen that will reduce the flaccidity of the tissues caused by loss of volume. The liquid, or liquefied fat, which flows into the surrounding tissue, is disposed of by the body.
Choosing one method rather than another depends on the cost, timing and situation of the individual patient.
Tissue stabilized guided subcision: the innovative FDA-approved treatment to combat cellulite in the long term
Tissue stabilized guided subcision is a new technique in which the fibrous septae, or the structural cause of cellulite, are severed and released to restore the smoothness of the skin surface. Treatment with tissue stabilized guided subcision is considered minimally invasive, because it is performed in an outpatient clinic, under local anaesthesia and recovery is more or less immediate. Through the use of a vacuum suction handpiece, the area to be treated is selected and lifted, allowing the doctor to work on stable tissue during incision.
This treatment allows the expert doctor to accurately sever the subcutaneous fibrous septae – which are responsible for the unsightly “orange peel” effect characteristic of cellulite – in a controlled way. The results are long-lasting – in fact, patients who have undergone the treatment still show satisfaction 3 years after the procedure.
About Dr. Gigliotti Diego
State Medical Board: 4673 Perugia
Dr. Diego Gigliotti is specialized in Emergency Surgery and First Aid. He’s a Professor at the Specialization Course in Hemodynamic Phlebology. Dr. Gigliotti is author of important scientific publications published in prestigious Italian and foreign magazines. He has also been guest on famous television programs of medicine and cosmetic surgery.